SOLVED SOME OF THE PROBLEM :
Problem 02: Initialize an integer array of 10 elements and print how many numbers are odd and how many numbers are even. For example, Input: 12 32 43 1 54 53 15 64 3 13 Output: 6 odd numbers 4 even numbers |
Solved of this problem : #include <iostream> #include <conio.h> using namespace std; int main() { int arr[100]; int i,size,odd=0,even=0; cout<<"Enter your arry size:"<<" "; cin>>size; cout<<"\nEnter elements of the array:"<<" "; for(i=0; i<size; i++) { cout<<"Enter the element arr["<<i<<"] :"; cin>>arr[i]; } for(i=0; i<size; i++) { if(arr[i]%2==0) { even++; } else{ odd++; } } cout<<"\nTotal even numbers of an array :"<<even<<"\n"; cout<<"Total odd numbers of an array : "<<odd; getch(); return 0; } |
Problem 03: Write a function that takes TWO parameters to print all the odd numbers between a given range. Input the starting value of the range and ending value of the range. Then, send them as the parameters to your function. For example, Output: Starting value: 12 Ending value: 23 13 15 17 19 21 23 |
Solved of this problem: #include<stdio.h> #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main(){
int number; int min,max; cout << "Enter the minimum range: "; cin >> min;
cout << "Enter the maximum range: "; cin >> max;
cout << "Odd numbers in given range are: "; for(number = min;number <= max; number++)
if(number % 2 !=0) cout << number<< " ";
printf("\nEven numbers in given range are: "); for(number = min;number <= max; number++)
if(number % 2 ==0) cout << number << " "; return 0; } Console output of this problem: |
Problem 04: Write a program to perform matrix addition between 3 matrices. For example, Input: 12 13 14 1 2 3 101 104 107 15 16 17 4 5 6 102 105 108 18 19 20 7 8 9 103 106 109 Output: 114 119 124 121 126 131 128 133 138 |
Solved of this problem: using namespace std; int main() { int m, n, c, d, first[10][10], second[10][10],third[10][10],sum[10][10]; cout << "Enter number of rows and columns of matrix:"<<" "; cin >> m >> n; cout << "Enter elements of first matrix:"<<" "; for (c = 0; c < m; c++) for (d = 0; d < n; d++) cin >> first[c][d]; cout << "Enter the elements of second matrix:"<<" "; for (c = 0; c < m; c++) for (d = 0; d < n; d++) cin >> second[c][d]; cout<<"Enter the elements of third matrix:"<<" "; for (c = 0; c < m; c++) for (d = 0; d < n; d++) cin >> third[c][d]; for (c = 0; c < m; c++) for (d = 0; d < n; d++) sum[c][d] = first[c][d] + second[c][d]+third[c][d]; cout << "Sum of the matrices:"<<" "; for (c = 0; c < m; c++) { for (d = 0; d < n; d++) cout << sum[c][d] << "\t"; cout << endl; } return 0; } |
Console Output of this problem: |
Problem 05: Write a function to calculate factorial of a given integer number if that number is a prime number. If it is not, it will give an error. For example, Scenario 1 Input: 5 Output: 120 Scenario 2 Input: 4 Output: Error! Not a prime number. |
Solved of this problem: #include <iostream> using namespace std; int functionOfPrimeNumber(int a) { int check =0; for(int i=2; i<3 ; i++) { if(a<2) { check =0; } else if(a%i!=0) { check= 1; } else { check=0; break; } } return check; } int functionOfFactorial(int a) { int Factorial=1; for(int counter=a; counter>=2; counter--) { Factorial=Factorial*counter; } return Factorial; } int main() { while(1){ int n; cout<<"Enter a integer number:"<<" "; cin>>n; if(functionOfPrimeNumber(n)==1) { cout<<n<< " is a Prime Number"<<endl; cout<< "Factorial of "<<n<<" is "<<functionOfFactorial(n)<<endl;} else cout<<"Error!"<<""<<n<<""<<" is not a prime number"<<endl; } } |
Console Output of This Problem : |
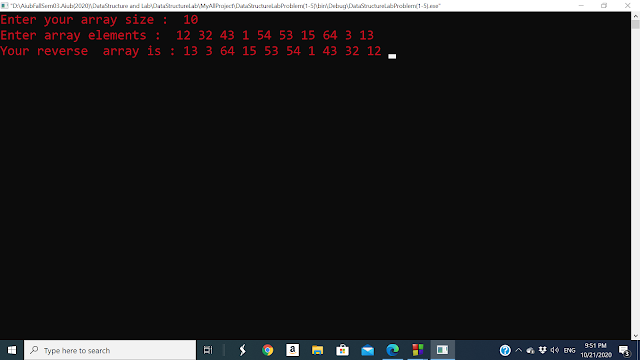
Problem 06: Initialize TWO integer arrays of different sizes. Merge the input arrays and create a new array. Then print the new array in reverse order. For example, Array_1 = {10,20,30,40,50} Array_2 = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8} Output: 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 50 40 30 20 10 |
Solved of this problem : #include <iostream> using namespace std; #include<conio.h> int main() { int firstArray[5],secondArray[8],margedArray[10]; int i=0,j=0,k=0; int InputOne,InputTwo,n; cout<<"Enter your first arry size: " <<" "; cin>>InputOne; cout<<"Enter your first arry elements:"<<" "; for(i=0;i<InputOne;i++) { cin>>firstArray[i]; } cout<<"Enter your second arry size: " <<" "; cin>>InputTwo; cout<<"Enter your second arry elements:"<<" "; for(i=0;i<InputTwo;i++) { cin>>secondArray[i]; } i=0; while(i<InputOne && j<InputTwo) { if(firstArray[i]<secondArray[j]) { margedArray[k++]=firstArray[i++]; } else { margedArray[k++]=secondArray[j++]; } } while(i<InputOne) { margedArray[k++]=firstArray[i++]; } while(j<InputTwo) { margedArray[k++]=secondArray[j++]; } cout<<"Your marged array is:"<<" "; for(k=0;k<InputOne+InputTwo;k++) { cout<<margedArray[k]<<" "; } cout<<endl; cout<<"Your reversed array is:"<<" "; for(int k=12;k>=0;k--) { cout<<margedArray[k]<<" "; } getch(); return 0; } Console Output of this code: |
Problem 07: Initialize TWO integer arrays A and B of different sizes. Make a new array with the common elements between A and B. Print the new array element(s). If there is no common element, output “No common element!”. For example, Scenario 1: Array_1 = {1,4,6,3,6,9} Array_2 = {5,3,7,1,2,6} Output: 1 6 3 Scenario 2: Array_1 = {1,4,6,3,6,9} Array_2 = {5,8,7,12,21,63} Output: No common element! |
Solved of this problem : #include<iostream> #include<conio.h> using namespace std; int main() { int n1,n2,i,j; cout<<"Enter your first array size: "<<" "; cin>>n1; int array1[n1]; /* Enter distinct elements */ cout<<"Enter the elements of the first array: "<<" "; for(i=0;i<n1;i++) { cin>>array1[i]; } cout<<"\nEnter your second array size: "<<" "; cin>>n2; int array2[n2]; cout<<"Enter the elements of the second array: "<<" "; for(i=0;i<n2;i++) { cin>>array2[i]; } /* printing elements that are common in both the arrays */ cout<<"\nYour common elements of the two arrays: "<<" "; for(i=0;i<n1;i++) { for(j=0;j<n2;j++) { if(array1[i]==array2[j]) { cout<<array1[i]<<" "; } } } getch(); return 0; } Console output of this problem: |
Problem 08: Initialize an array. Size should be more than FIVE. Write you program to change the array in such a way so that there cannot be any duplicate element in the array anymore. Print the changed array. If the initialized array already had no duplicate elements from the beginning, output a message saying “Array already unique!”; For example, Scenario 1: Array_1 = {1,4,6,3,6,9,1} Output: 1 4 6 3 9 Scenario 2: Array_1 = {1,4,5,3,6,9} Output: Array already unique! |
Solved of this problem: #include<iostream> #include<conio.h> using namespace std; int main() { int i,j,k,n,a[30]; cout<<"Enter your array size:"<<" "; cin>>n; cout<<"\nEnter elements of array:"<<" "; for(i=0;i<n;++i) { cin>>a[i]; } for(i=0;i<n;++i) { for(j=i+1;j<n;) { if(a[i]==a[j]) { for(k=j;k<n-1;++k) a[k]=a[k+1]; --n; } else ++j; } } cout<<"Your array elements without any duplicates elements:"<<" "; for(i=0;i<n;++i) { cout<<a[i]<<" "; } cout<<endl; for(int i=0; i<n; i++) { if(a[i]==n) { cout<<"Array already unique."<<endl; break; } } getch(); return 0; } |
Problem 09: Initialize an integer array A of size 10. Take an integer as input and print how many times that integer occurs in A. For example, Array_1 = {8,4,6,1,6,9,6,1,9,8} Output: Input a number to search: 6 The number occurs 3 times in the array |
Solved of this problem: #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int array[10],dup[10]; int size,i,j,InputNumber; cout<<"Enter your array size:"<<" "; cin>>size; cout<<"Enter your array elements:"<<" "; for(i=0; i<size; i++) { cin>>array[i]; dup[i]=-1; } for(i=0; i<size; i++) { int cnt=1; for(j=i+1; j<size; j++) { if(array[i]==array[j]) { cnt++; dup[j]=0; } } if(dup[i]!=0) { dup[i]=cnt; } } cout<<"Enter a integer number from array :"<<" "<<endl; cin>>InputNumber; for(i=0; i<=1; i++) { if(InputNumber==array[i]) { cout<<"your number"<<" "<<array[i]<<" "<<" occured"<<" "<<dup[i]<<" "<<"times"<<endl; } } return 0; } |
Your whole Screenshot here: (Console Output): |
Problem 10: Initialize an integer array of size 10. Print the number of times each element occurs in the array. For example, Array_1 = {8,4,6,1,6,9,6,1,9,8} Output: 8 occurs = 2 times 4 occurs = 1 time 6 occurs = 3 times 1 occurs = 2 times 9 occurs = 2 times |
Solved of this problem is: #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int array[25],dup[25]; int size,i,j,cnt; cout<<"Enter your array size:"<<" "; cin>>size; cout<<"Enter your array elements:"<<" "; for(i=0; i<size; i++) { cin>>array[i]; dup[i]=-1; } for(i=0; i<size; i++) { cnt=1; for(j=i+1; j<size; j++) { if(array[i]==array[j]) { cnt++; dup[j]=0; } } if(dup[i]!=0) { dup[i]=cnt; } } cout<<"Duplicates elements in array:"<<" "<<endl; for(i=0; i<size; i++) { if(dup[i]!=0) { cout<<"Your Number is"<<" "<<array[i]<<endl; cout<<"your number"<<" "<<array[i]<<" "<<" occured"<<" "<<dup[i]<<" "<<"times"<<endl; } } return 0; } |
For example,
Matrix_1:
1 6 7 9
2 4 8 5
3 1 9 4
Output:
1 2 3
6 4 1
7 8 9
9 5 4
Write a function named encode that takes TWO parameters, a string s and an integer j.
Skip j number of characters in the string and increase the ASCII value of the next character by 2.
Perform step (ii) throughout the string.
For example,
Sample String (s): I am a student
Sample Integer (j): 2
Converted String: I cm c student











.jpeg)








No comments:
Post a Comment